Craig F Powers
age ~63
from Fremont, CA
- Also known as:
-
- Craig E Powers
Craig Powers Phones & Addresses
- Fremont, CA
- Oakland, CA
- 11546 323Rd St, Auburn, WA 98092 • 2538040787
- 1421 Elm St, Auburn, WA 98092 • 2538040787
- 11503 321St St, Auburn, WA 98092 • 2538332178
- Livermore, CA
- Ogden, UT
- Kiona, WA
- Corvallis, OR
- Smithville, MO
- 11546 SE 323Rd Pl, Auburn, WA 98092 • 2538040787
Work
-
Company:Sb nationAug 2012
-
Position:News desk contributor
Education
-
School / High School:Washington State University- Pullman, WAAug 2003
-
Specialities:B.A. in History
Ranks
-
Licence:Washington - Active
-
Date:1979
Resumes

Software Development Engineer
view sourcePosition:
Software Development Engineer at SKF
Location:
Fort Collins, Colorado
Industry:
Machinery
Work:
SKF - Fort Collins, Colorado Area since Nov 2011
Software Development Engineer
Advanced Energy - Fort Collins, Colorado Area Apr 2006 - Oct 2011
RF match design engineer
Advanced Energy Jan 1999 - Mar 2006
Staff Test Engineer
Advanced Energy Apr 1995 - Jan 1999
HALT / HASS test engineer
Storage Technology Incorporated May 1991 - Mar 1995
Test Engineer
Software Development Engineer
Advanced Energy - Fort Collins, Colorado Area Apr 2006 - Oct 2011
RF match design engineer
Advanced Energy Jan 1999 - Mar 2006
Staff Test Engineer
Advanced Energy Apr 1995 - Jan 1999
HALT / HASS test engineer
Storage Technology Incorporated May 1991 - Mar 1995
Test Engineer
Education:
Colorado State University 2006 - 2012
MSEE, (Electrical Engineering) Colorado State University 1986 - 1991
BSEE, (Electrical Engineering)
MSEE, (Electrical Engineering) Colorado State University 1986 - 1991
BSEE, (Electrical Engineering)
Skills:
Labview
Matlab
Green Belt
MathCAD
Python
C
C++
Visual C++
C#
VHDL
RF
Electrical Engineering
Test Automation
Simulation
Embedded Systems
Product Development
Analog
Software Development
Software Engineering
Power Electronics
Engineering Management
I2C
.NET
Matlab
Green Belt
MathCAD
Python
C
C++
Visual C++
C#
VHDL
RF
Electrical Engineering
Test Automation
Simulation
Embedded Systems
Product Development
Analog
Software Development
Software Engineering
Power Electronics
Engineering Management
I2C
.NET

Craig Powers
view sourceLocation:
United States

Craig Powers Burlington, VT
view sourceWork:
SB Nation
Aug 2012 to 2000
News Desk Contributor CougCenter.com
Mar 2009 to 2000
Managing Editor College Basketball Prospectus
Nov 2012 to Nov 2012
Author Office of Sustainability, University of Vermont
Burlington, VT
Sep 2011 to May 2012
Communications Intern Monroe Harding
Nashville, TN
Apr 2010 to Aug 2011
Education Specialist First Choice In-Home Care
Bellevue, WA
Nov 2008 to Jul 2009
Supervisor of Direct Care
Aug 2012 to 2000
News Desk Contributor CougCenter.com
Mar 2009 to 2000
Managing Editor College Basketball Prospectus
Nov 2012 to Nov 2012
Author Office of Sustainability, University of Vermont
Burlington, VT
Sep 2011 to May 2012
Communications Intern Monroe Harding
Nashville, TN
Apr 2010 to Aug 2011
Education Specialist First Choice In-Home Care
Bellevue, WA
Nov 2008 to Jul 2009
Supervisor of Direct Care
Education:
Washington State University
Pullman, WA
Aug 2003 to Dec 2007
B.A. in History
Pullman, WA
Aug 2003 to Dec 2007
B.A. in History
Lawyers & Attorneys

Craig Lee Powers, Tacoma WA - Lawyer
view sourceAddress:
Roller Vernon & Powers Inc PS
Po Box 8220, Tacoma, WA 98418
2534751225 (Office)
Po Box 8220, Tacoma, WA 98418
2534751225 (Office)
Licenses:
Washington - Active 1979
Us Patents
-
Database Repository With Deferred Transactions
view source -
US Patent:6480847, Nov 12, 2002
-
Filed:Jan 29, 1999
-
Appl. No.:09/240733
-
Inventors:Terris J. Linenbach - San Mateo CA
Vladimir Gorelik - Fremont CA
Craig R. Powers - Belmont CA
Robert E. Powers - Fremont CA
Tana C. Netsch - Santa Clara CA -
Assignee:Sagent Technology, Inc. - Mountain View CA
-
International Classification:G06F 1730
-
US Classification:707 8, 707200, 707203, 707100, 7071041, 707201, 711148, 711149, 711150, 711151, 711152, 711168
-
Abstract:A deferred transaction mechanism facilitates multi-threaded operation of database application programs. The deferred transaction mechanism allows data items to be committed from the local memory of a computer system to a database system in a background thread, while other foreground threads continue to read the data item. In most instances, this makes the delay in committing a data item to the database imperceptible to a human user of a database application program. The deferred transaction mechanism further supports an âundoâ feature, which allows modifications to a data item located in a computers local memory to be rapidly discarded.
-
Method And Apparatus For Processing Data Using Multi-Tier Caching
view source -
US Patent:6651142, Nov 18, 2003
-
Filed:May 5, 2000
-
Appl. No.:09/565874
-
Inventors:Vladimir Gorelik - Palo Alto CA
Glenn A. Shapland - Santa Clara CA
Craig R. Powers - San Carlos CA -
Assignee:Sagent Technology - Mountain View CA
-
International Classification:G06F 1300
-
US Classification:711119, 711122, 711132
-
Abstract:A method and apparatus for processing data using multi-tier caching are described. In one embodiment, the method includes receiving a user request containing one or more data parameters and searching cache memories of multiple tiers until finding a parameterized result set associated with the data parameters. The multiple tiers correspond to stages in the transformation of data retrieved from one or more data sources according to the user request. Once the parameterized result set associated with the data parameters is found, it is used to create a final result set.
-
Method And Apparatus For Creating A Lineage Of A Data Field In A Data Flow System
view source -
US Patent:7117219, Oct 3, 2006
-
Filed:May 5, 2000
-
Appl. No.:09/565775
-
Inventors:Craig R. Powers - San Carlos CA, US
Vladimir Gorelik - Palo Alto CA, US -
Assignee:Group 1 Software, Inc. - Lanham MD
-
International Classification:G06F 17/00
-
US Classification:707101, 705 35
-
Abstract:A method and apparatus for creating a lineage for a data field is disclosed. The method may include creating a unique identifier for a data field. Also, a record of the origin of data is created when the data is inserted into the data field; however this is not required. The record of the origin of data is associated with the unique identifier for the data field. The lineage for the data field may be viewed. In so doing, the transformations to the data field may be shown.
-
Architecture For General Purpose Near Real-Time Business Intelligence System With Client Devices And Methods Therefor
view source -
US Patent:7243124, Jul 10, 2007
-
Filed:Nov 5, 2002
-
Appl. No.:10/289139
-
Inventors:Kenneth C. Gardner - Menlo Park CA, US
Tim J. Beauchamp - Belmont CA, US
Tana Christine Netsch - Campbell CA, US
Geoffrey Deane Owen Nicholls - Palo Alto CA, US
Craig R. Powers - San Francisco CA, US -
Assignee:Oracle International Corporation - Redwood Shores CA
-
International Classification:G06F 15/16
-
US Classification:709205
-
Abstract:A method of transferring a set of data elements to a recipient on a network, the network includes a set of devices registered to the recipient. The method also includes receiving the set of data elements. The method further includes ascertaining if the first device is present on the network and if the first user is available via the first device based on status information received via set network. If the first device is present on the network and if the first user is available via the first device, the method includes transferring the set of set of data elements to the first device. And, if the first device is not present on the network or if the first user is not available via the first device, the method further includes transferring the set of set of data elements to the second device if the second device is present on the network and if the first user is available via the second device.
-
Architecture For General Purpose Near Real-Time Business Intelligence System And Methods Therefor
view source -
US Patent:7272660, Sep 18, 2007
-
Filed:Nov 5, 2002
-
Appl. No.:10/289131
-
Inventors:Craig R. Powers - San Francisco CA, US
Kenneth C. Gardner - Menlo Park CA, US
Tim J. Beauchamp - Belmont CA, US
Tana Christine Netsch - Campbell CA, US
Geoffrey Deane Owen Nicholls - Palo Alto CA, US -
Assignee:Oracle International Corporation - Redwood Shores CA
-
International Classification:G06F 15/173
-
US Classification:709238, 709231, 370338
-
Abstract:A method of optimizing the delivery of a set of data elements to a device, the set of data elements further comprising a metadata portion. The method further includes determining a source of each element of the set of data elements, and creating a set of rules for transforming the set of data elements from a first representation to a second representation, based in part on the metadata. The method further includes transferring the set of data elements from the source to a first computer, transforming the set of data elements, based in part on the set of rules, and delivering the second representation to the device. Thereafter, the method includes monitoring the source for a change to the set of data elements. And, if required, the method further includes transferring the change from the source to the first computer.
-
Method And Apparatus For Distributed Rule Evaluation In A Near Real-Time Business Intelligence System
view source -
US Patent:7412481, Aug 12, 2008
-
Filed:Nov 5, 2002
-
Appl. No.:10/289142
-
Inventors:Geoffrey Deane Owen Nicholls - Palo Alto CA, US
Craig R. Powers - San Francisco CA, US
Kenneth C. Gardner - Menlo Park CA, US
Tana Christine Netsch - Campbell CA, US
Tim J. Beauchamp - Belmont CA, US -
Assignee:Oracle International Corporation - Redwood Shores CA
-
International Classification:G06F 15/16
G06F 15/173 -
US Classification:709204, 709224
-
Abstract:A method for optimally monitoring a set of data elements for an event. The method includes determining a set of data elements, each of which further comprises a state. An event is commonly a change in this state. The method further includes creating a rule for monitoring the event, wherein the rule comprises an event identification portion resident on a first computer and an action portion resident on a second computer. The method also includes monitoring the set of data elements for the event based, in part, on the event identification portion, and determining if the event has occurred. If so, the method further includes sending the set of data elements to the second computer. The method also includes executing a set of actions, based in part, on the action portion. Thereafter, the method further includes monitoring the set of data elements based, in part, on the rule.
-
Enterprise Link For A Software Database
view source -
US Patent:7454423, Nov 18, 2008
-
Filed:Sep 6, 2002
-
Appl. No.:10/237559
-
Inventors:Craig R. Powers - San Francisco CA, US
Kenneth C. Gardner - Menlo Park CA, US -
Assignee:Oracle International Corporation - Redwood Shores CA
-
International Classification:G06F 17/00
-
US Classification:707 10, 707101, 707102, 707103 X, 7071041, 709223
-
Abstract:An enterprise link for a software database is coupled to existing enterprise systems within an organization and also to an active data cache. The enterprise link contains an active designer whereby a user is able to create one or more data flow definitions on how to operate on data stored in the enterprise systems as the data in those systems changes. The transformed data is transmitted to a data flow service in the enterprise link in real-time where it is made available to end-users in the active data cache.
-
Method And Apparatus For Ensuring Accountability In The Examination Of A Set Of Data Elements By A User
view source -
US Patent:7668917, Feb 23, 2010
-
Filed:Nov 5, 2002
-
Appl. No.:10/289155
-
Inventors:Tana Christine Netsch - Campbell CA, US
Geoffrey Deane Owen Nicholls - Palo Alto CA, US
Craig R. Powers - San Francisco CA, US
Kenneth C. Gardner - Menlo Park CA, US
Tim J. Beauchamp - Belmont CA, US -
Assignee:Oracle International Corporation - Redwood Shores CA
-
International Classification:G06F 15/16
-
US Classification:709206, 709203, 709207
-
Abstract:A method for substantially assuring the examination of a set of data elements by a first user with a messaging device, the set of data elements further comprising a metadata portion. The method further includes determining a set of data elements, each data element of the set of data elements further comprising a state. The method also includes creating a first set of rules for monitoring a change to the state, creating a second of rules for transforming the set of data elements from a first representation to a second representation, based in part on the metadata, and creating a third set of rules for optimizing the delivery of a notification to the first user, based in part on the first set of rules, the notification further comprising a link to the second representation. The method further includes sending the notification to the first user based in part on the third set of rules. And, if the first user does not redeem the second representation, the method includes sending the notification to a second user.
Name / Title
Company / Classification
Phones & Addresses
Vice President
Roller Vernon & Powers Inc PS
Attorneys. Attorneys - Insurance Law. Attorneys - Personal Injury & Property Damage. Attorneys - Wills. Trust & Probate. Attorneys - Business Law/Corporation/Partnership. Attorneys - Product Liability
Attorneys. Attorneys - Insurance Law. Attorneys - Personal Injury & Property Damage. Attorneys - Wills. Trust & Probate. Attorneys - Business Law/Corporation/Partnership. Attorneys - Product Liability
1001 S 38Th St, Tacoma, WA 98418
2534751225, 2534732084
2534751225, 2534732084
Vice President
Roller Vernon Powers Larson & Ellington Inc Ps
Attorney
Attorney
1001 S 38 St, Tacoma, WA 98418
PO Box 8220, Tacoma, WA 98419
2534751225, 2534732084
PO Box 8220, Tacoma, WA 98419
2534751225, 2534732084
Principal
Craig L Powers Attorney
Legal Services Office
Legal Services Office
1001 S 38 St, Tacoma, WA 98418
Ipo Edge, LLC
Financial Software · Business Services at Non-Commercial Site · Nonclassifiable Establishments
Financial Software · Business Services at Non-Commercial Site · Nonclassifiable Establishments
1956 Las Gallinas Ave, San Rafael, CA 94903
Systems Support Manager
Coit Services
Drycleaning Plant Carpet/Upholstery Cleaning · Uphol Cln-Cust Premis · Building Maintenance Svc Repair Services Carpet/Upholstery Clean Tile/Marble Contractor · Carpet and Upholstery Cleaning Services
Drycleaning Plant Carpet/Upholstery Cleaning · Uphol Cln-Cust Premis · Building Maintenance Svc Repair Services Carpet/Upholstery Clean Tile/Marble Contractor · Carpet and Upholstery Cleaning Services
16750 Woodinville Redmond Rd Ne Ste C102, Woodinville, WA 98072
16750 Woodinville Redmond Rd NE, Woodinville, WA 98072
4254819505, 4254861510
16750 Woodinville Redmond Rd NE, Woodinville, WA 98072
4254819505, 4254861510
Plaxo

CRAIG POWERS
view sourceRetired but p/t Wheelchair van driver at Hulmes

craig powers
view source
Craig Powers
view sourceFM Global

Craig Powers
view sourceManager at Sprint

Craig Powers
view sourceWoodstock, CT
Classmates

Craig Powers
view sourceSchools:
Wappingers High School Wappingers Falls NY 1989-1993
Community:
Fred Coritz, Douglas Kendall, Jack Campbell, James Sauter

Craig Powers
view sourceSchools:
Central Valley High School Central Valley CA 1981-1985
Community:
Christine Blue, Kelli Ashford, Bruce Smith

Craig Powers
view sourceSchools:
Craneville Elementary School Dalton MA 1980-1985, Center School Dalton MA 1981-1982, Nessacus Middle School Dalton MA 1985-1989
Community:
Toni Moulton, Wes Ferrin, Sandra Dill, Mike Pezzo

Craig Powers
view sourceSchools:
East Longmeadow High School East Longmeadow MA 1974-1978
Community:
Susan Reed, Mike Maloni

Craig Powers
view sourceSchools:
Burch High School Delbarton WV 1980-1984
Community:
Donna Erskine, Melissa Diamond

Craig Powers
view sourceSchools:
Minnechaug Regional High School Wilbraham MA 1974-1978
Community:
Joanne Novak, Michele Dollar, Ruth Fortini, Mark Bates

Craig Powers
view sourceSchools:
Minnechaug Regional High School Wilbraham MA 1974-1978
Community:
Craig Powers, Michele Dollar, Ruth Fortini, Mark Bates
Youtube
Myspace
Googleplus
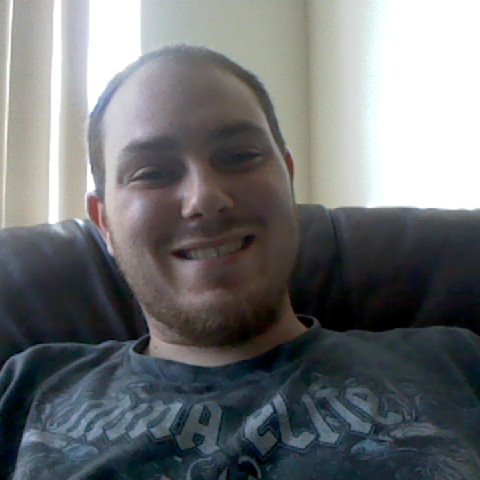

Craig Powers
Education:
California State University, Sacramento - Criminal Justice, California State University, Stanislaus - Criminal Justice, California State University, Chico - Criminal Justice, Solano Community College - Administration of Justice
Craig Powers

Craig Powers

Craig Powers

Craig Powers

Craig Powers

Craig Powers

Craig Powers

Craig F Powers Sr.
view source
Craig Powers
view source
Craig M. Powers
view source
Craig A Powers
view source
Craig Stephen Powers
view source
Christine Craig Powers
view source
Craig Powers
view source
Craig Powers
view sourceFlickr
News

NCAA Tournament 2013: Florida Gulf Coast makes first March Madness ...
view source- tournament. It was hosted at Mercer, the No. 1 seed, giving them a home-court advantage in what was hypothetically a neutral site tournament, part of why Craig Powers had the Bears as the heavy favorites to win the tourney. Unsurprisingly, the top two teams ended up matched against each other in the finals.
- Date: Mar 19, 2013
- Category: Sports
- Source: Google

Pac-12 Network: What it Means for WSU
view source- Craig Powers ,*0=w4qkojhhr1+gDndwfuhkr1Bgwnqkojhhr1?g+n{lh.r@0g0n0lw,"+"u+kD1dgfnh,r..+4Dldwfuhkr1@g{n,.@~l5,.0>w4qkojhhr1+gln3?l>u@i+*r@>>*>{_%d%"+"?,2A%2#A__sjd_iq:1:;1fl:py2oqdfh2vhrdllvpjfpq2lrd1er1wqqfv24sgw2%=kw__u@#_"+"_f%vr_l_oqdfh0_l%pv_d_f@%v#o__vu#_lhwxovdkh#_l%pw_d_j@l
- Date: Jul 28, 2011
- Category: Sports
- Source: Google
Get Report for Craig F Powers from Fremont, CA, age ~63



















