Mark L Mcauliffe
age ~59
from San Francisco, CA
- Also known as:
-
- Mark Lawrence Mcauliffe
- Mark L Wiener
- Mark L Weiner
Mark Mcauliffe Phones & Addresses
- San Francisco, CA
- 185 Heather Ln, Palo Alto, CA 94303 • 6505658895
- East Palo Alto, CA
- Madison, WI
- 1787 Lark Ln, Sunnyvale, CA 94087 • 4089968979
- Menlo Park, CA
- Rochester, MN
- Santa Clara, CA
- 2 Townsend St APT 4-301, San Francisco, CA 94107
Work
-
Position:Administrative Support Occupations, Including Clerical Occupations
Education
-
Degree:High school graduate or higher
Us Patents
-
Database Management System With Efficient Version Control
view source -
US Patent:7243088, Jul 10, 2007
-
Filed:Aug 6, 2003
-
Appl. No.:10/636361
-
Inventors:Sanjay Verma - Foster City CA, US
Mark L. McAuliffe - Palo Alto CA, US
Sherry Listgarten - Palo Alto CA, US
Sibsankar Haldar - Madhyamgram, IN -
Assignee:Oracle International Corporation - Redwood Shores CA
-
International Classification:G06F 11/00
G06F 17/30 -
US Classification:707 1, 714 16
-
Abstract:A two copy versioning scheme is proposed. The scheme provides efficient implementation for a high read load database and eliminates read dependencies. The versioning scheme provides efficient implementation for transactions executing under ANSI READ COMMITTED isolation, and is extensible to serializable isolation. The two-copy versioning scheme is garbage free meaning that all versions of data records are used during execution and is adapted to index scanning operations. A “deferred delete” scheme allows read transactions to complete data deallocation operations. Statements that require “snapshots” are efficiently supported.
-
Operating Logging For Online Recovery In Shared Memory Information Systems
view source -
US Patent:7739244, Jun 15, 2010
-
Filed:Oct 14, 2004
-
Appl. No.:10/966285
-
Inventors:Sanjay Verma - Foster City CA, US
Mark Lawrence McAuliffe - Palo Alto CA, US
Kirk Meredith Edson - Fremont CA, US -
Assignee:Oracle International Corporation - Redwood Shores CA
-
International Classification:G06F 17/30
-
US Classification:707684, 707685, 714 19
-
Abstract:Clients are permitted to directly attach to a client server system. An oplog management system tracks changes as clients make the changes to control structures of the direct connection client server system. The Oplogging system stores changes in oplogs. Then, if a client fails, the Oplogging system can repair the control structures, either by undoing the changes made by the client, or else completing the changes in place of the client; depending upon principles defined.
-
Database Management System With Efficient Version Control
view source -
US Patent:8010497, Aug 30, 2011
-
Filed:Jun 1, 2007
-
Appl. No.:11/757224
-
Inventors:Sanjay Verma - Foster City CA, US
Mark L. McAuliffe - Palo Alto CA, US
Sherry Listgarten - Palo Alto CA, US
Sibsankar Haldar - Madhyamgram, IN -
Assignee:Oracle International Corporation - Redwood Shores CA
-
International Classification:G06F 7/00
-
US Classification:707662, 707661, 707667
-
Abstract:A two copy versioning scheme is proposed. The scheme provides efficient implementation for a high read load database and eliminates read dependencies. The versioning scheme provides efficient implementation for transactions executing under ANSI READ COMMITTED isolation, and is extensible to serializable isolation. The two-copy versioning scheme is garbage free meaning that all versions of data records are used during execution and is adapted to index scanning operations. A “deferred delete” scheme allows read transactions to complete data deallocation operations. Statements that require “snapshots” are efficiently supported.
-
User-Defined Parallelization In Transactional Replication Of In-Memory Database
view source -
US Patent:20120284228, Nov 8, 2012
-
Filed:May 5, 2011
-
Appl. No.:13/101783
-
Inventors:Sourav Ghosh - Union City CA, US
Rohan Aranha - Redwood City CA, US
Tirthankar Lahiri - Palo Alto CA, US
Mark McAuliffe - Palo Alto CA, US
Chih-Ping Wang - Palo Alto CA, US
Paul Tuck - Swindon, GB
Nagender Bandi - Foster City CA, US
John E. Miller - Los Altos CA, US
Dina Thomas - Palo Alto CA, US
Marie-Anne Neimat - Atherton CA, US -
International Classification:G06F 17/30
-
US Classification:707615, 707E17005
-
Abstract:A replication track is a designated group of transactions that are to be replicated at a destination database in a way that, with respect to any other transaction in the replication track, preserves transactional dependency. Further, transactions in a replication track can be replicated at the destination database without regard to transactional dependency of other transactions in another track. This facilitates concurrent parallel replication of transactions of different tracks. Replicating data in this manner is referred to herein as track replication. An application may request execution of transactions and designate different tracks for transactions.
-
Column Domain Dictionary Compression
view source -
US Patent:20130060780, Mar 7, 2013
-
Filed:Sep 2, 2011
-
Appl. No.:13/224327
-
Inventors:Tirthankar Lahiri - Palo Alto CA, US
Dina Thomas - Palo Alto CA, US
Kirk Meredith Edson - Fremont CA, US
Subhradyuti Sarkar - Fremont CA, US
Mark McAuliffe - Palo Alto CA, US
Marie-Anne Neimat - Atherton CA, US
Chih-Ping Wang - Palo Alto CA, US -
Assignee:ORACLE INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION - Redwood Shores CA
-
International Classification:G06F 17/30
-
US Classification:707741, 707E17037
-
Abstract:In column domain dictionary compression, column values in one or more columns are tokenized by a single dictionary. The domain of the dictionary is the entire set of columns. A dictionary may not only map a token to a tokenized value, but also to a count (“token count”) of the number of occurrences of the token and corresponding tokenized value in the dictionary's domain. Such information may be used to compute queries on the base table.
-
Power Loss Protection Based On Write Requirements
view source -
US Patent:20220365678, Nov 17, 2022
-
Filed:Jul 15, 2022
-
Appl. No.:17/865854
-
Inventors:- Mountain View CA, US
Brandon Davis - Mountain View CA, US
Mark L. McAuliffe - San Francisco CA, US
Benjamin Scholbrock - San Jose CA, US
Zoltan DeWitt - Daly City CA, US
Phillip Hord - Mountain View CA, US
Ronald Karr - Palo Alto CA, US -
International Classification:G06F 3/06
G06F 12/02 -
Abstract:A storage system and related method are for operating solid-state storage memory in a storage system. Zones of solid-state storage memory are provided. Each zone includes a portion of the solid-state storage memory. The zone has a data write requirement for the zone for reliability of data reads. The storage system adjusts power loss protection for at least one zone. The adjusting is based on the data write requirement for the zone and responsive to detecting a power loss.
-
Metadata Management In A Storage System
view source -
US Patent:20220269417, Aug 25, 2022
-
Filed:Feb 9, 2022
-
Appl. No.:17/667756
-
Inventors:- MOUNTAIN VIEW CA, US
RICHARD HANKINS - SAN JOSE CA, US
MARK McAULIFFE - SAN FRANCISCO CA, US
NEIL VACHHARAJANI - MENLO PARK CA, US -
International Classification:G06F 3/06
G06F 12/02
G06F 12/121 -
Abstract:A system and method for efficiently maintaining metadata stored among a plurality of solid-state storage devices. A data storage subsystem supports multiple mapping tables. Records within a mapping table are arranged in multiple levels. Each level stores at least pairs of a key value and a physical pointer value. The levels are sorted by time. New records are inserted in a created new highest (youngest) level. No edits are performed in-place. A data storage controller determines both a cost of searching a given table exceeds a threshold and an amount of memory used to flatten levels exceeds a threshold. In response, the controller incrementally flattens selected levels within the table based on key ranges. After flattening the records in the selected levels within the key range, the records may be removed from the selected levels. The process repeats with another different key range.
-
Data Rebuild When Changing Erase Block Sizes During Drive Replacement
view source -
US Patent:20210365190, Nov 25, 2021
-
Filed:Aug 9, 2021
-
Appl. No.:17/396882
-
Inventors:- Mountain View CA, US
Timothy W. Brennan - San Francisco CA, US
Mark L. McAuliffe - San Francisco CA, US
Neil Buda Vachharajani - Menlo Park CA, US -
International Classification:G06F 3/06
G06F 12/10 -
Abstract:A method for rebuilding data when changing erase block sizes in a storage system is provided. The method includes determining one or more erase blocks to be rebuilt and allocating one or more replacement erase blocks, wherein the one or more erase blocks and the one or more replacement erase blocks have differing erase block sizes. The method includes mapping logical addresses, for the one or more erase blocks, to the one or more replacement erase blocks and rebuilding the one or more erase blocks into the one or more replacement erase blocks, in accordance with the mapping.
Resumes

Mark Mcauliffe
view sourceLocation:
San Francisco, CA
Industry:
Construction
Work:
Leprechaun Wood
Contractor
Contractor

Software Engineer
view sourceLocation:
1982 west Bayshore Rd, East Palo Alto, CA 94303
Industry:
Computer Software
Work:
Oracle Jul 2005 - Dec 2010
Consulting Member of Technical Staff
Pure Storage Jul 2005 - Dec 2010
Software Engineer
Consulting Member of Technical Staff
Pure Storage Jul 2005 - Dec 2010
Software Engineer
Education:
University of Wisconsin - Madison 1989 - 1997
Doctorates, Doctor of Philosophy, Computer Science Oberlin College 1985 - 1989
Bachelors, Bachelor of Arts, Computer Science
Doctorates, Doctor of Philosophy, Computer Science Oberlin College 1985 - 1989
Bachelors, Bachelor of Arts, Computer Science
Skills:
Unix
Software Development
Scalability
Linux
Distributed Systems
Software Engineering
Python
Debugging
Multithreading
Algorithms
Computer Science
Software Design
Software Development
Scalability
Linux
Distributed Systems
Software Engineering
Python
Debugging
Multithreading
Algorithms
Computer Science
Software Design

Mark Mcauliffe
view source
Mark Mcauliffe
view source
Mark Mcauliffe
view source
Mark Mcauliffe
view source
Mark Mcauliffe
view sourceFlickr
Youtube
Classmates

Mark McAuliffe
view sourceSchools:
Shaler Area Intermediate School Glenshaw PA 1974-1978
Community:
William Bartholomew, Steven Peters

Shaler Area Intermediate ...
view sourceGraduates:
Eric Weihrauch (1982-1986),
Mark McAuliffe (1974-1978),
Dan Poslusney (1963-1967),
Caroline Reno (1979-1983),
Terry Sedam (1968-1972)
Mark McAuliffe (1974-1978),
Dan Poslusney (1963-1967),
Caroline Reno (1979-1983),
Terry Sedam (1968-1972)

Mark McAuliffe
view source
Mark McAuliffe
view source
Mark McAuliffe
view source
Mark Mac McAuliffe
view source
Mark McAuliffe
view source
Mark McAuliffe
view source
Mark McAuliffe
view source
Mark McAuliffe
view sourceGoogleplus
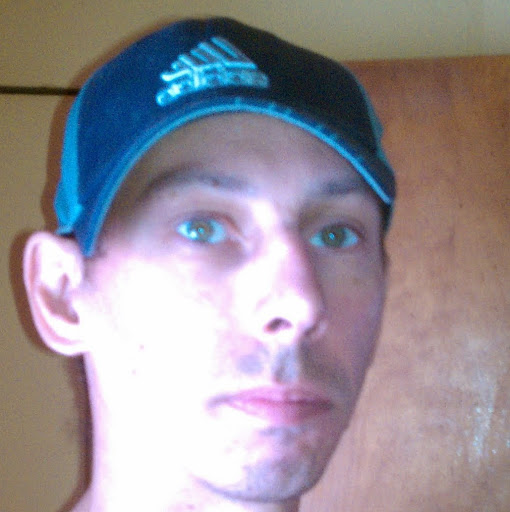

Mark Mcauliffe
Education:
Hilton Head High School

Mark Mcauliffe
Tagline:
Computer Geek/Gamer, 501st Stormtrooper, Fantasy Reader, RPG Gamer

Mark Mcauliffe

Mark Mcauliffe

Mark Mcauliffe

Mark Mcauliffe

Mark Mcauliffe
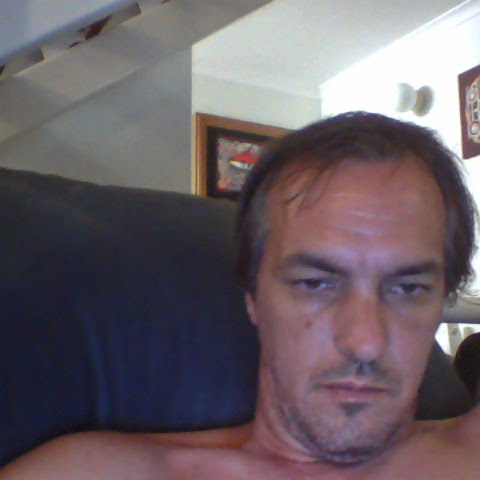

Mark Mcauliffe
Plaxo

Mark McAuliffe
view sourceDirector at Be Healthy acupuncture and holistic he...
Myspace
Get Report for Mark L Mcauliffe from San Francisco, CA, age ~59